
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, User Experience (UX) design is paramount to the success of any product, whether it’s a website, app, or any other digital interface. UX design focuses on creating seamless, intuitive, and enjoyable user interactions. But what exactly does UX design entail, and why is it so crucial?
Understanding UX Design
At its essence, UX design is about providing meaningful and relevant experiences to users. It requires deeply understanding of users’ needs, behaviours, and emotions. UX design is not solely concerned with aesthetics but prioritizes functionality and usability, ensuring that every interaction in the user journey is smooth and satisfying.
By incorporating user feedback and iterative testing, UX designers create intuitive interfaces that anticipate and solve potential issues. Ultimately, UX design aims to enhance user satisfaction and loyalty by making products easy and enjoyable to use.
Key Principles of UX Design
Understanding and implementing these fundamental principles can greatly improve the overall user experience.
- User-Centered Design
- Simplicity and Clarity
- Consistency
- Feedback and Responsiveness
- Accessibility
These principles ensure that users have a seamless and enjoyable experience, enhancing both usability and satisfaction. By prioritizing these elements, designers can create intuitive and accessible interfaces that cater to a diverse audience.
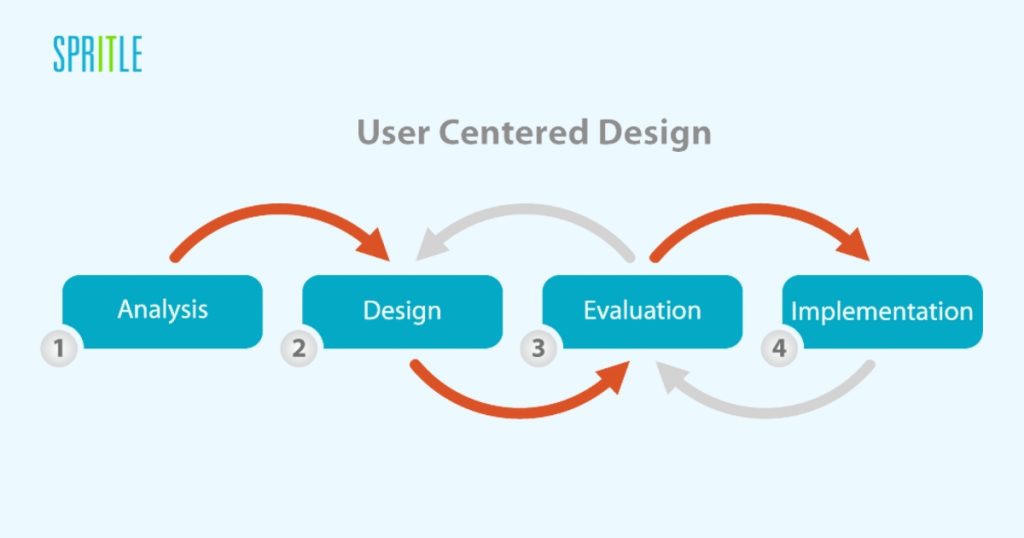
1. User-Centered Design
User-centered design is the foundation of UX. It involves conducting extensive user research, creating personas, and engaging in usability testing to understand users’ needs and preferences. By designing with the user in mind, products can be tailored to meet their expectations effectively.
2. Simplicity and Clarity
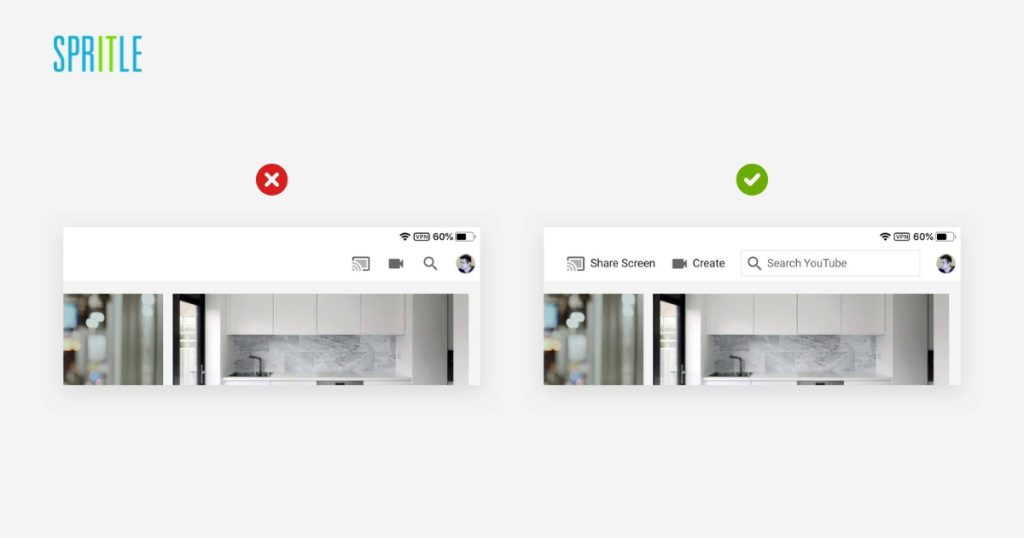
A clean, uncluttered interface helps users navigate easily and find what they need quickly. Clear design elements and straightforward navigation reduce cognitive load, making the user experience more intuitive.
3. Consistency
Consistent design elements such as fonts, colors, and buttons help users familiarise themselves with the interface, enhancing predictability and usability. Consistency across a product’s design ensures a cohesive user experience and minimizes confusion.

4. Feedback and Responsiveness
Providing feedback is essential to guiding users and confirming their actions. Whether through animations indicating a button press or notifications for completed actions, responsive feedback helps users understand the system’s status and their interactions with it.

5. Accessibility
Designing for accessibility ensures that products are usable by everyone, including those with disabilities. This includes considerations for screen readers, keyboard navigation, and ensuring sufficient color contrast. Accessible design is not just ethical but also broadens the potential user base.
The UX Design Process
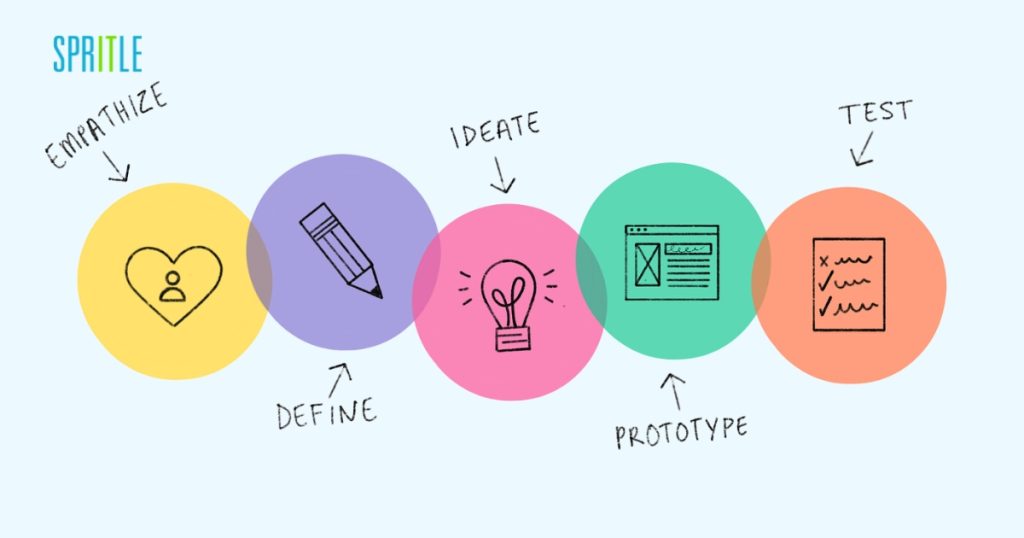
A well-structured UX design process is crucial for creating products that connect with users and meet their requirements successfully. The UX design process is iterative and involves several key stages:
- Research
- Design
- Testing
- Implementation
- Evaluation
1. Research
Research is the first step in the UX design process. Designers gather information about users, their needs, and their interactions with similar products through surveys, interviews, focus groups, and usability tests. This helps them understand the user and the problem. They also study competitors, analyze market trends, and collect feedback to ensure their designs are effective and user-friendly. This research helps create designs that meet users’ needs and expectations.
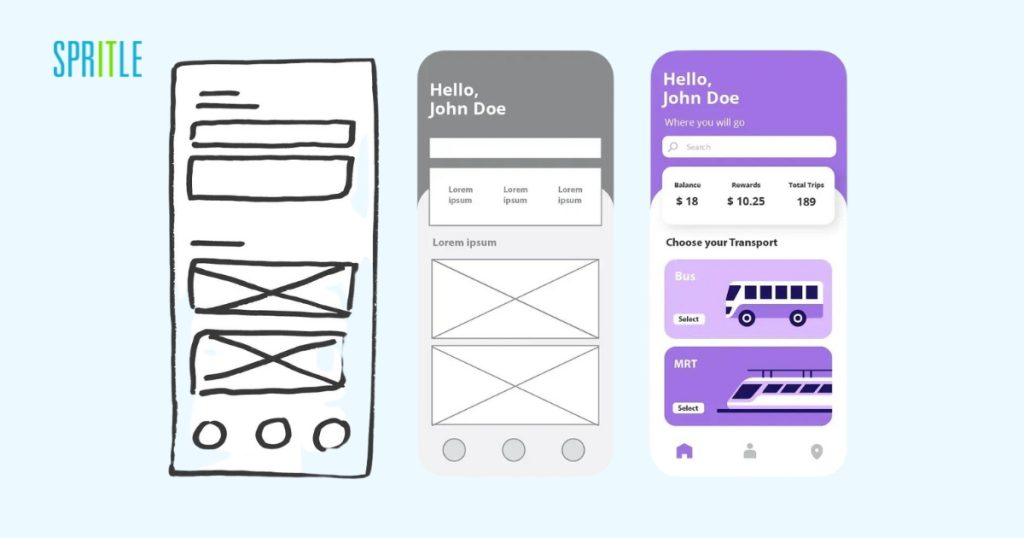
2. Design
In the design phase, designers create wireframes and prototypes based on insights from the research phase. Wireframes are basic layouts that outline the structure of a product, while prototypes are interactive models that simulate the user experience. This phase focuses on creating an intuitive and functional design that meets user needs.
3. Testing
Testing is a critical phase where prototypes are tested with real users to gather feedback. Usability testing helps identify any issues or areas for improvement. This phase is iterative, with multiple rounds of testing and refinement to ensure the design is effective and user-friendly.
4. Implementation
Research is the first and most crucial step in the UX design process. Designers gather information about users, their needs, and how they interact with similar products using surveys, interviews, and usability tests. This helps them create designs that truly meet users’ needs.
Once the design is approved, designers work with developers to ensure it is built correctly. Developers provide real-time feedback on the design, and together they make adjustments to keep it user-friendly and practical. This teamwork is essential for creating a successful product.
5. Evaluation
After the product is launched, it’s continuously evaluated and refined based on user feedback and performance metrics. Post-launch evaluations help identify any remaining issues and provide opportunities for further improvements.
Tools of the Trade
UX designers use a variety of tools to create and refine their designs. Some popular tools include:

- Sketch and Figma: These are powerful tools for creating wireframes and prototypes. They offer collaborative features that enable team members to work together seamlessly.
- InVision: This tool allows for interactive prototyping and collaboration. It’s particularly useful for getting stakeholder feedback and testing user interactions.
- Adobe XD: A comprehensive design tool that integrates well with other Adobe products, making it ideal for designers already using Adobe’s suite.
- UserTesting: A platform for conducting usability tests and gathering user feedback. It helps designers understand how real users interact with their designs.
The Future of UX Design
As technology evolves, so does UX design. Some emerging trends include:
- Voice User Interfaces (VUIs): With the rise of smart speakers and virtual assistants, designing for voice interactions is becoming increasingly important. VUIs offer new challenges and opportunities for creating intuitive user experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can enhance UX by personalizing user experiences and automating repetitive tasks. AI-driven analytics can provide deeper insights into user behavior, helping designers create more targeted and effective designs.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These technologies offer immersive and engaging user experiences. Designing for AR and VR requires a different approach, focusing on 3D interactions and spatial design.

Conclusion
UX design is a dynamic field that prioritizes the user at every stage. By focusing on user needs, simplifying interactions, and staying updated with trends, UX designers create exceptional experiences. Embracing UX principles helps designers create products that resonate with users and stand out digitally.
